Page 112 - 2596-CA SR Lanka- Annual Report 2022
P. 112
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
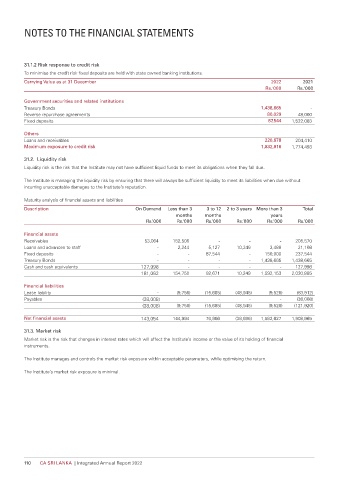
31.1.2 Risk response to credit risk
To minimise the credit risk fixed deposits are held with state owned banking institutions.
Carrying Value as at 31 December 2022 2021
Rs.'000 Rs.'000
Government securities and related institutions
Treasury Bonds 1,438,665 -
Reverse repurchase agreements 80,029 48,000
Fixed deposits 87,544 1,522,083
Others
Loans and receivables 226,678 204,410
Maximum exposure to credit risk 1,832,916 1,774,493
31.2. Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Institute may not have sufficient liquid funds to meet its obligations when they fall due.
The Institute is managing the liquidity risk by ensuring that there will always be sufficient liquidity to meet its liabilities when due without
incurring unacceptable damages to the Institute’s reputation.
Maturity analysis of financial assets and liabilities
Description On Demand Less than 3 3 to 12 2 to 3 years More than 3 Total
months months years
Rs.’000 Rs.’000 Rs.’000 Rs.’000 Rs.’000 Rs.’000
Financial assets
Receivables 53,064 152,506 - - - 205,570
Loans and advances to staff - 2,244 5,127 10,249 3,488 21,108
Fixed deposits - - 87,544 - 150,000 237,544
Treasury Bonds - - - - 1,438,665 1,438,665
Cash and cash equivalents 127,998 - - - - 127,998
181,062 154,750 92,671 10,249 1,592,153 2,030,885
Financial liabilities
Lease liability - (9,756) (15,685) (48,945) (9,526) (83,912)
Payables (38,008) - - - - (38,008)
(38,008) (9,756) (15,685) (48,945) (9,526) (121,920)
Net financial assets 143,054 144,994 76,986 (38,696) 1,582,627 1,908,965
31.3. Market risk
Market risk is the risk that changes in interest rates which will affect the Institute’s income or the value of its holding of financial
instruments.
The Institute manages and controls the market risk exposure within acceptable parameters, while optimising the return.
The Institute’s market risk exposure is minimal.
110 CA SRI LANKA | Integrated Annual Report 2022